中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (25): 4644-4651.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.25.012
• 药物控释材料 drug delivery materials • 上一篇 下一篇
半乳糖化海藻酸钠与海藻酸钠何种质量比可保障微胶囊的力学稳定?
田 猛1, 2, 3,韩 波3,游 潮1,万昌秀2
- 1四川大学华西医院神经外科,四川省成都市 610041
2四川大学高分子科学与工程学院生物医学工程系,四川省成都市 610065
3南加州大学Keck医学院外科系,美国加利福利亚州洛杉矶市 90032
Galactosylated alginate and sodium alginate: What is the optimal mass ratio for maintaining the mechanical stability?
Tian Meng1, 2, 3, Han Bo3, You Chao1, Wan Chang-xiu2
- 1 Department of Neurosurgery, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
2 Department of Biomedical Engineering, College of Polymer Science & Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, Sichuan Province, China
3 Department of Surgery, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles 90032, CA, USA
摘要:
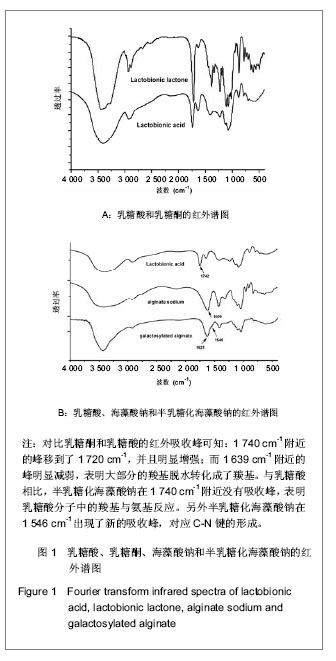
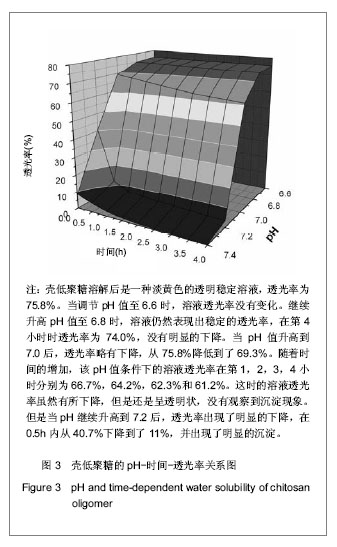
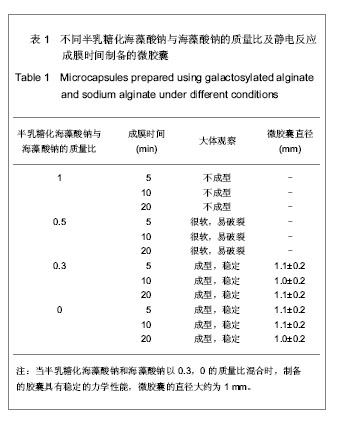
背景:大量研究表明经过半乳糖修饰的材料可以显著改善肝细胞的黏附能力,进而影响肝细胞的形态和功能。静电复合制备的微胶囊被广泛应用于细胞包裹、酶固定和药物包埋等诸多领域,但国内外未见以壳低聚糖和海藻酸钠制备微胶囊用于肝细胞包裹的研究。 目的:制备一种新型用于肝细胞包裹的半乳糖化海藻酸钠-壳低聚糖微胶囊。 方法:对海藻酸钠进行半乳糖化修饰,红外光谱、核磁共振谱和元素分析表征半乳糖化海藻酸钠的合成。浊度法研究壳低聚糖的水溶性。采用一步法制备半乳糖化海藻酸钠-壳低聚糖微胶囊,研究制备过程中半乳糖化海藻酸钠含量(半乳糖化海藻酸钠与海藻酸钠的质量比分别为100%,50%,30%,0)和静电反应成膜时间(5,10,20 min)对微胶囊的影响。 结果与结论:对于半乳糖化海藻酸钠的合成,红外光谱表明了羧基峰的消失和C-N键的形成;核磁共振谱表明产物中不但出现了乳糖酸中对应的峰,而且还偶合了一部分碳二亚胺的分子链;元素分析计算出半乳糖接枝含量为20%,偶合到海藻酸钠分子链中的碳二亚胺含量为8%。半乳糖修饰对微胶囊制备的影响为:半乳糖的引入在一定程度上削弱了海藻酸钠分子链上负电荷的密度,影响了静电复合成膜的过程。结果表明只有当半乳糖化海藻酸钠与海藻酸钠以小于1∶1的质量比混合时,才能得到力学稳定的微胶囊。
中图分类号:



.jpg)